David Li, PhD

Postdoctoral Research Fellow, University of Pennsylvania
Doctor of Philosophy, Carnegie Mellon University
Master of Science, Boston University
Bachelor of Science, Johns Hopkins University

Postdoctoral Research Fellow, University of Pennsylvania
Doctor of Philosophy, Carnegie Mellon University
Master of Science, Boston University
Bachelor of Science, Johns Hopkins University
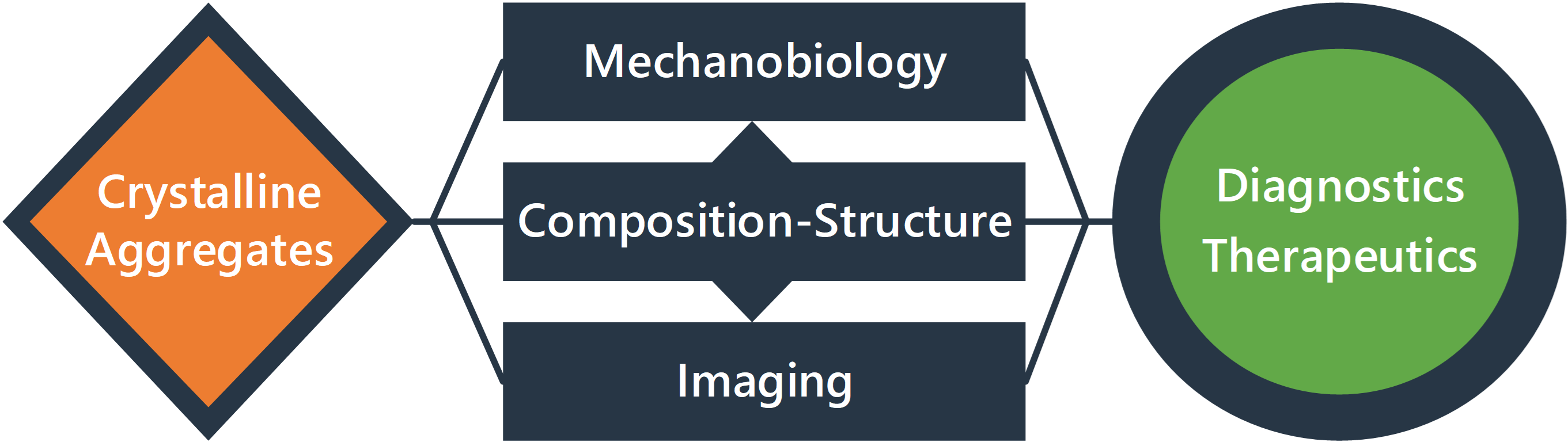
I am a postdoctoral research fellow pursuing a tenure-track faculty position in biomedical engineering, bioengineering, mechanical engineering, and allied fields in the biomedical sciences. My research centers on the biomechanics and mechanobiology of cells and tissues, with a focus on how they intersect with metabolism and other aspects of physiology and pathology. A major thrust of my future research is on crystalline aggregates of cholesterol and cholesterol esters, which likely play critical roles in a wide range of diseases such as metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver diseases (MASLD), atherosclerosis, and preeclampsia. These stiff crystalline aggregates likely drive disease progression through unknown, but critical, pathogenic effects on cell and tissue mechanics and mechanobiology. In addition to mechanistic studies on these topics, I aim to translate these findings into novel diagnostics and therapeutics by leveraging my unique combination of expertise in specialized imaging and biocompatible microfabrication.
My postdoctoral work in the lab of Dr. Rebecca G. Wells at the University of Pennsylvania focuses on the relationship between lipid crystallization and tissue mechanics in hepatic steatosis and fibrosis. The main thrust of my work uses multiple modes of imaging and mechanical characterization of histological features in liver tissue, along with microfabrication of model tissue systems, to determine that dietary cholesterol storage-related lipid crystal formation stiffens hepatic tissue (now published in bioRxiv). I have received the gracious support of both an NRSA T32 Postdoctoral Fellowship Award and the 2023 Postdoctoral Research Fellowship Award from the American Liver Foundation for this work.
Working with Dr. Wells and in collaboration with Dr. Paul A. Janmey, I developed a technique to associate tissue mechanics with histology at the mesoscale, and have published in FASEB Bioadvances how liver fat accumulation causes softening on the macro and meso scales. In my doctoral work with Dr. Yu-li Wang at Carnegie Mellon University, I discovered that cells coordinate collective movement through Wnt signaling, published in PNAS. While training with Dr. Joyce Y. Wong at Boston University, I studied biomimetic microfabrication of silk in collaboration with Dr. David. L. Kaplan, published in Biofabrication.
If interested, please reach me at: David.Li@pennmedicine.upenn.example.edu